Turning discarded plastic into fuel? Creating a circular economy where waste plastic resources are reused.
2023. 05. 11
2023. 05. 11
The cement industry plays a crucial role in construction, producing around 4.1 billion tons globally in 2020, according to the US Geological Survey. However, concerns about the environmental impact of cement production are mounting.
To address this issue, LG Chem has teamed up with several Korean companies and associations, including Sampyo Cement, Hyundai Rotem, the Korean Engineers Alliance, and the Korea Cement Association. The goal of this collaboration is to use waste plastic as a fuel in the cement calcination process and recycle the resulting chlorine dust to promote resource circularity. What benefits can be expected from this joint effort, and what are the plans for achieving a more sustainable future?
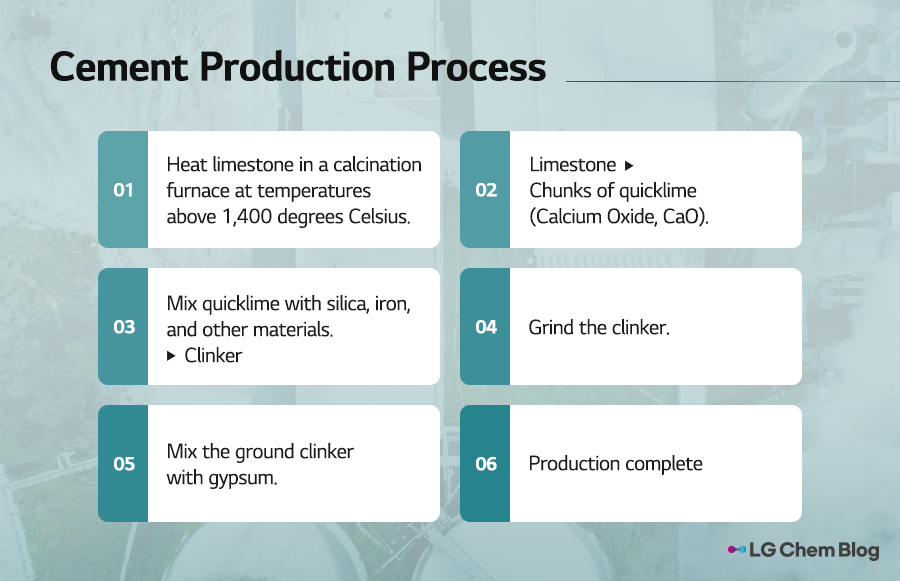
Before exploring how waste plastic can be used in , let’s take a closer look at the cement manufacturing process. In the calcination furnace, limestone (CaCO₃) is heated to temperatures exceeding 1,400 degrees Celsius, producing quicklime (CCaO). The quicklime is then mixed with silica, iron, and other materials to create clinker, which is crushed after it cools. Gypsum is added to the crushed clinker, resulting in the cement commonly known.
Unfortunately, calcination typically relies on fossil fuels like bituminous coal, which generates carbon dioxide. To address this issue, waste tires and plastic have been used as fuel alternatives to achieve carbon neutrality. By incorporating waste plastic into the calcination process, resources can be recycled while also reducing greenhouse gas emissions. A study by Professor Jae-Geun Bae from the Department of Environmental Engineering at Seoul National University of Science and Technology found that using waste materials as raw materials and fuel for cement production could potentially reduce greenhouse gas emissions by around 2.68 million tons per year and save approximately annually in fuel import costs.

While many cement companies still use bituminous coal as their primary fuel source, there is a growing trend of using waste plastics as fuel due to their high biomass content and potential to address waste disposal issues. However, there are challenges associated with this approach. One of the main concerns is the generation of chlorine dust during the combustion of waste plastics.

Chlorine dust is a waste material generated during the combustion of plastic waste that can be difficult to recycle and often ends up in landfills. When waste plastics are incinerated as fuel in cement plants, chlorine dust can accumulate on the preheater walls, obstructing the flow of raw materials and decreasing operational efficiency. One of the reasons for the collaboration among LG Chem, Sampyo Cement, Hyundai Rotem, the Korean Engineers Alliance, and the Korea Cement Association is to address the issue of chlorine dust and make it easier to recycle.
Hyundai Rotem is partnering with Anytech, a specialized environmental equipment company in Korea, to establish resource circulation facilities and apply resource circulation technology. This technology converts chlorine dust into potassium chloride (KCI), a raw material used in fertilizer production. Moreover, this process can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by utilizing carbon dioxide generated during cement production. By improving recycling and reducing emissions, cement manufacturing facilities are expected to become more sustainable.

LG Chem aims to employ process technologies that combine chemical and physical methods to prevent chlorine from adhering to the inside of the furnace and to enhance the stability of the potassium chloride resource utilization facility. Additionally, LG Chem plans to develop high-value-added products such as potassium hydroxide (KOH) and potassium carbonate (K2CO3), which are used as semiconductor cleaning materials. To achieve this, they aim to increase the purity of potassium chloride (KCI) produced by the resource utilization process for chlorine dust. This collaboration is expected to help develop these materials domestically, as the production of potassium, which is the raw material for potassium hydroxide and potassium carbonate, is challenging domestically and Korea is entirely dependent on imports.
Based on this collaboration, Sampyo Cement plans to more actively utilize waste plastics as alternative fuels. They also plan to optimize the mineralization process of both chlorine dust and carbon dioxide generated during cement production, as well as the evaporation and concentration process for the production of potassium chloride. They will promote zero-waste landfilling based on these efforts. The Korean Engineers Alliance plans to propose effective policies for resource circulation to the government, local governments, and public agencies, and continuously raise awareness of the importance and necessity of resource circulation through lectures and events. The Korea Cement Association plans to expand the waste plastic resource platform being developed to the entire cement industry.
Several industry companies and associations, including LG Chem, Sampyo Cement, Hyundai Rotem, Korean Engineers Alliance, and Korea Cement Association, have come together to promote the use of plastic waste as fuel and collaborate on solutions to the challenges faced in the process, such as the treatment of chlorine dust. They aim to accelerate the advancement of plastic waste-to-fuel technology.
LG Chem aims to create a circular economy for plastic waste by developing and implementing technologies that promote resource circulation and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. LG Chem is committed to working with their partners to create a better future.
There are no comments yet! Be the first to let us know your thoughts!